AFRICA Listing Details
Africa listing details. ProdAfrica Business Directory is the best way to make business in Africa. We connect Europe and Africa. Your listing is visible now.
VERIFIED LISTING PUBLIC COMPANY OR LOCATIONValue sectors where we participate
Specializations or competitive advantages
Who we are
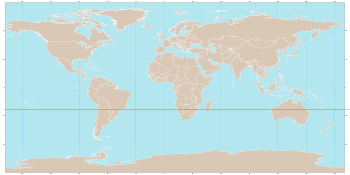
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point on the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be directly overhead. Its northern equivalent is the Tropic of Cancer.
The Tropic of Capricorn is one of the five major circles of latitude that mark maps of the Earth. As of 23 December 2016, its latitude is 23°26′13.5″ (or 23.43708°) south of the equator, but it is very gradually moving northward, currently at the rate of 0.47 arcseconds, or 15 metres, per year.
Geography and environment
The Tropic of Capricorn is the dividing line between the Southern Temperate Zone to the south and the tropics to the north. The northern hemisphere equivalent of the Tropic of Capricorn is the Tropic of Cancer.
The position of the Tropic of Capricorn is not fixed, but rather it varies in a complex manner over time; see under circles of latitude for information.
In Australia, areas on the Tropic have some of the most variable rainfall in the world and thus even the wetter areas cannot be generally farmed, since irrigation sources invariably dry up in drought years. In southern Africa, where rainfall is more reliable, farming is possible, though yields are low even with fertilisers.
In South America, whilst in the continental cratons soils are almost as old as in Australia and Southern Africa, the presence of the geologically young and evolving Andes means that this region is on the western side of the subtropical anticyclones and thus receives warm and humid air from the Atlantic Ocean. As a result, areas in Brazil adjacent to the Tropic are extremely important agricultural regions, producing large quantities of crops such as sugarcane, and the natural rainforest vegetation has been almost entirely cleared, except for a few remaining patches of Atlantic Forest. In and west of the Andes, however, the Humboldt Current makes conditions extremely arid, creating the Atacama Desert, one of the driest in the world, so that no glaciers exist between Volcán Sajama at 18˚30’S and Cerro Tres Cruces at 27˚S. Vegetation here is almost non-existent, though on the eastern slopes of the Andes rainfall is adequate for rainfed agriculture.