Religion has played a significant role in the history and culture of Africa, with the continent being home to a diverse range of religions and belief systems. The religious landscape of Africa is diverse, with traditional African religions, Christianity, Islam, and other religions all having a significant presence on the continent.
Traditional African Religions:
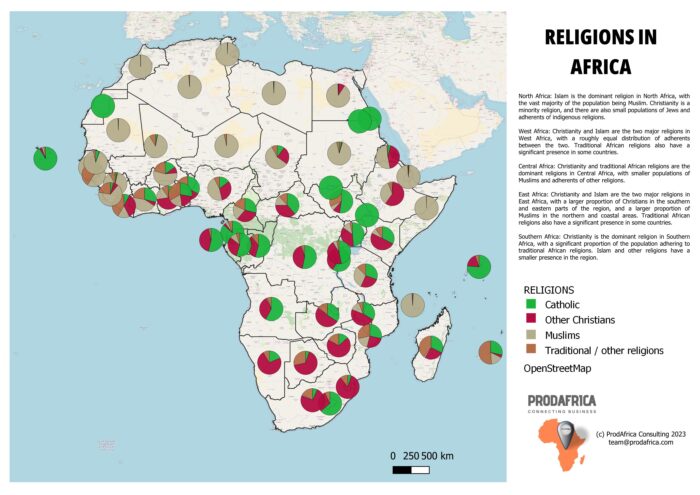
Traditional African religions are the indigenous religions of Africa that were practiced by the people of Africa before the introduction of Christianity and Islam. These religions are based on the worship of the ancestors and the belief in the existence of a Supreme Being or creator. Traditional African religions vary widely across the continent, with each culture having its own unique beliefs and practices. However, there are some commonalities across different traditional African religions, such as the belief in the interconnectedness of all things and the importance of ancestral worship.
Christianity:
Christianity was first introduced to Africa by European missionaries in the 1st century. Today, Christianity is one of the most widely practiced religions in Africa, with approximately 541 million Christians on the continent. The spread of Christianity in Africa was largely facilitated by colonialism and the activities of European missionaries. The largest Christian denominations in Africa are Roman Catholicism, Anglicanism, and various Protestant denominations. In some African countries, such as Ethiopia, Christianity has coexisted with traditional African religions for centuries, resulting in unique syncretic religious practices.
Islam:
Islam was introduced to Africa in the 7th century through the spread of Arab traders and later through the activities of Islamic missionaries. Today, Islam is the second-largest religion in Africa, with approximately 414 million Muslims on the continent. Islam has had a significant impact on African culture and history, particularly in North and East Africa. The spread of Islam in Africa was facilitated by trade, migration, and the activities of Islamic scholars and missionaries. The largest Islamic denomination in Africa is Sunni Islam, followed by Shia Islam and Sufism.
Other Religions:
In addition to traditional African religions, Christianity, and Islam, there are also other religions that have a significant presence in Africa, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, and Sikhism. These religions were introduced to Africa through trade, migration, and the activities of religious scholars and missionaries.
Religious Tolerance and Conflict:
Religious tolerance and conflict have been significant issues in Africa throughout its history. Religious conflicts in Africa are often intertwined with political and social issues and are exacerbated by factors such as economic inequality, ethnic and regional tensions, and competition for resources. Religious conflicts in Africa have taken various forms, including interfaith conflicts, conflicts between different religious denominations, and conflicts between religious and secular authorities.
Africa has long been known for its conflicts and wars, many of which have been attributed to religious differences. The continent is home to a diverse range of religious beliefs and practices, including Christianity, Islam, traditional African religions, and others. These religions have often been a source of tension and conflict, leading to violence and bloodshed in various parts of Africa.
One of the most notable examples of religious conflict in Africa is the ongoing conflict between Christians and Muslims in Nigeria. The conflict dates back to the early 2000s and has been characterized by acts of terrorism, bombings, and attacks on places of worship. The Boko Haram militant group has been at the forefront of the conflict, with its aim of establishing an Islamic caliphate in Nigeria.
Similarly, the conflict in Sudan has also been linked to religious differences, with the predominantly Muslim north of the country often at odds with the mostly Christian south. The Sudanese civil war, which began in 1983 and lasted for over two decades, claimed the lives of over 2 million people and was one of the deadliest conflicts in African history.
Religious tensions have also fueled conflicts in other parts of Africa, including the Central African Republic, Ethiopia, and the Democratic Republic of Congo. In the Central African Republic, the conflict between Christians and Muslims has led to a humanitarian crisis, with widespread violence and displacement of civilians. In Ethiopia, tensions between the Orthodox Christian and Muslim communities have led to violence and unrest, while in the Democratic Republic of Congo, religious differences have contributed to ongoing conflicts and instability in the region.
It is important to note that while religious differences have often been cited as a primary cause of conflict in Africa, they are often intertwined with other factors, including political and economic issues. Nevertheless, the role of religion in fueling conflicts cannot be ignored, and efforts to promote interfaith dialogue and understanding are crucial in resolving the conflicts that plague the continent.
The conflicts and wars in Africa are complex and multifaceted, with religion often playing a significant role. The diverse religious beliefs and practices on the continent have often been a source of tension and conflict, leading to violence and bloodshed. Efforts to promote peace and understanding between different religious communities are crucial in resolving the conflicts that continue to plague Africa.

Team ProdAfrica
team@prodafrica.com




