Africa is a continent rich in resources and potential, with a population of over 1.3 billion people. However, it is also a continent with its fair share of challenges, including poverty, unemployment, and economic inequality. In the face of these challenges, entrepreneurship has emerged as a key driver of growth and development across the continent. In this article, we will explore the role of entrepreneurs in Africa, the challenges they face, and the opportunities that lie ahead.
The Role of Entrepreneurs in Africa
Entrepreneurship is a critical component of economic growth and development. Entrepreneurs create new businesses, products, and services, and they generate jobs and income for themselves and others. In Africa, entrepreneurship has played an important role in driving economic growth and development, especially in sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and technology.
One of the key benefits of entrepreneurship in Africa is its ability to create jobs. With high levels of youth unemployment, entrepreneurship has become a viable option for many young people. According to the World Bank, Africa’s labor force is expected to grow by more than 1 billion people over the next decade, creating a massive demand for jobs. By creating new businesses and hiring employees, entrepreneurs can help to address this demand and reduce unemployment.
Entrepreneurship in Africa has also led to innovation and technological advancement. Entrepreneurs are often at the forefront of new technologies, developing new products and services that are not only innovative but also meet the needs of local communities. For example, entrepreneurs in Africa have developed mobile banking services, renewable energy solutions, and e-commerce platforms that are tailored to local needs and preferences.
Challenges Faced by Entrepreneurs in Africa
Despite the potential benefits of entrepreneurship in Africa, there are also significant challenges that entrepreneurs face. One of the biggest challenges is access to capital. Many entrepreneurs in Africa struggle to access the financing they need to start and grow their businesses. This is often due to a lack of access to traditional financing options such as banks and investors, as well as a lack of collateral and credit history.
Another challenge faced by entrepreneurs in Africa is a lack of infrastructure. In many countries, infrastructure is underdeveloped, making it difficult for entrepreneurs to transport goods, access markets, and connect with customers. This can be a significant barrier to entry for entrepreneurs, especially those in remote or rural areas.
Regulatory and legal challenges also pose a significant barrier to entrepreneurship in Africa. Many countries have complex and restrictive business regulations, which can make it difficult for entrepreneurs to start and grow their businesses. In addition, corruption and bureaucratic inefficiencies can make it difficult for entrepreneurs to navigate the regulatory landscape and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
Opportunities for Entrepreneurship in Africa
Despite these challenges, there are also significant opportunities for entrepreneurship in Africa. One of the most promising areas is the agriculture sector. With over 60% of Africa’s population engaged in agriculture, there is enormous potential for entrepreneurs to create new businesses and services that support the sector. This includes everything from food processing and storage to distribution and marketing.
Another promising area is technology. Africa has seen significant growth in the technology sector in recent years, with the rise of mobile technology and the internet. Entrepreneurs in Africa are leveraging these technologies to develop innovative solutions that are tailored to local needs and preferences. For example, mobile banking services have become increasingly popular across the continent, providing access to financial services for millions of people who previously had no access to traditional banking.
Entrepreneurship has emerged as a critical driver of growth and development in Africa. Entrepreneurs create jobs, drive innovation, and stimulate economic growth in a variety of sectors. However, they also face significant challenges, including a lack of access to capital, infrastructure, and regulatory barriers. Despite these challenges, there are also significant opportunities for entrepreneurship in Africa, particularly in the agriculture and technology sectors.
To support entrepreneurship in Africa, there are several steps that governments and other stakeholders can take. One of the most important is to improve access to financing for entrepreneurs. This could involve expanding microfinance and other alternative financing options, as well as providing tax incentives and other financial support for small businesses.
Improving infrastructure is also critical. This could involve investing in roads, ports, and other transport infrastructure, as well as expanding access to reliable electricity and internet connectivity. By improving infrastructure, entrepreneurs will be better able to access markets, connect with customers, and grow their businesses.
Finally, addressing regulatory and legal barriers is also critical. This could involve streamlining business regulations, reducing corruption, and improving the efficiency of government services. By making it easier for entrepreneurs to start and grow their businesses, governments can help to stimulate economic growth and development across the continent.
Entrepreneurs in Africa are the engine of growth. Despite the challenges they face, they are creating new businesses, products, and services that are driving economic growth and development across the continent. By supporting entrepreneurship in Africa, governments and other stakeholders can help to unlock the full potential of the continent and create a brighter future for all Africans.
| Statistic | Data | Data Source |
|---|---|---|
| Number of entrepreneurs in Africa | 80 million | International Labour Organization (ILO) |
| Percentage of adults in Africa who are entrepreneurs | 25% | Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) Africa Report 2018/2019 |
| Percentage of female entrepreneurs in Africa | 38% | GEM Africa Report 2018/2019 |
| Percentage of entrepreneurs in Africa who start their own business out of necessity | 69% | GEM Africa Report 2018/2019 |
| Percentage of entrepreneurs in Africa who have access to finance | 15% | World Bank Enterprise Surveys |
| Top industries for entrepreneurs in Africa | Agriculture, technology, retail | GEM Africa Report 2018/2019 |
| Number of tech hubs in Africa | 600+ | Disrupt Africa Tech Hubs Report 2021 |
| Percentage of global startup investment going to Africa | 1% | Partech Africa Annual Report 2021 |
| Top countries for entrepreneurship in Africa | Nigeria, Ghana, Botswana, Uganda | GEM Africa Report 2018/2019 |
This table provides some key insights into the state of entrepreneurship in Africa, along with their respective sources. It highlights the significant number of entrepreneurs in Africa, as well as the challenges they face in terms of access to finance. It also showcases the importance of female entrepreneurship in Africa and the prevalence of entrepreneurship out of necessity.
The table also provides some insights into the top industries for entrepreneurship in Africa, as well as the growth of the technology sector on the continent. Finally, it highlights the significant potential for entrepreneurship in Africa, as well as some of the top countries for entrepreneurship on the continent.
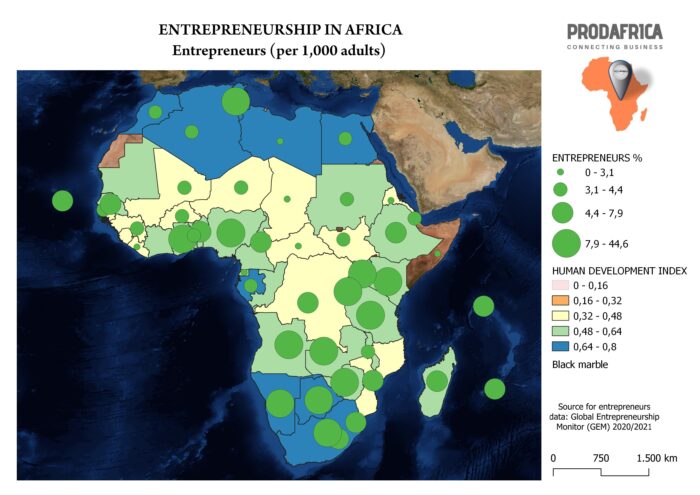
| ISO 3166-1 alpha-2 code | Country name | Estimated number of early-stage entrepreneurs per 1,000 adults |
|---|---|---|
| DZ | Algeria | 3.4 |
| AO | Angola | 39.4 |
| BJ | Benin | 4.6 |
| BW | Botswana | 41.3 |
| BF | Burkina Faso | 3.1 |
| BI | Burundi | N/A |
| CM | Cameroon | 6.9 |
| CV | Cape Verde | 7.2 |
| CF | Central African Republic | 2.5 |
| TD | Chad | 1.7 |
| KM | Comoros | N/A |
| CD | Democratic Republic of the Congo | 6.7 |
| DJ | Djibouti | 3.7 |
| EG | Egypt | 3.3 |
| GQ | Equatorial Guinea | 2.2 |
| ER | Eritrea | 2.7 |
| ET | Ethiopia | 5.5 |
| GA | Gabon | 4.1 |
| GM | Gambia | 3.8 |
| GH | Ghana | 13.3 |
| GN | Guinea | 3.2 |
| GW | Guinea-Bissau | N/A |
| KE | Kenya | 16.9 |
| LS | Lesotho | 5.7 |
| LR | Liberia | 2.9 |
| LY | Libya | N/A |
| MG | Madagascar | 5.3 |
| MW | Malawi | 3.5 |
| ML | Mali | 4.4 |
| MR | Mauritania | N/A |
| MU | Mauritius | 7.2 |
| MA | Morocco | 3.3 |
| MZ | Mozambique | 5.3 |
| NA | Namibia | 9.2 |
| NE | Niger | 4.4 |
| NG | Nigeria | 44.6 |
| RW | Rwanda | 8.4 |
| ST | Sao Tome and Principe | N/A |
| SN | Senegal | 7.9 |
| SC | Seychelles | 7.1 |
| SL | Sierra Leone | N/A |
| SO | Somalia | 2.2 |
| ZA | South Africa | 11.3 |
| SS | South Sudan | 3.1 |
| SD | Sudan | 3.9 |
| SZ | Eswatini | 7.3 |
| TZ | Tanzania | 11.4 |
| TG | Togo | 4.0 |
| TN | Tunisia | 8.4 |
| UG | Uganda | 19.3 |
| ZM | Zambia | 8.0 |
| ZW | Zimbabwe | 15.8 |
Global Entrepreneurship Monitor (GEM) Africa Report 2018/2019

Team ProdAfrica
team@prodafrica.com