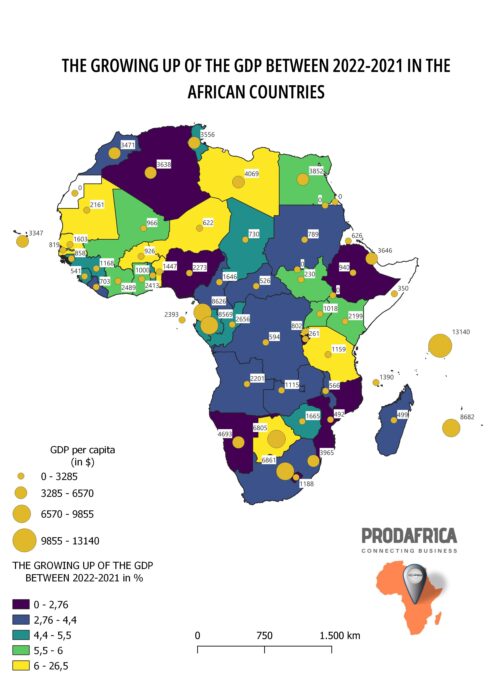
The GDP growth rates in African countries between 2021 and 2022 have been quite diverse, with some countries experiencing robust growth while others have experienced negative or sluggish growth. Nonetheless, the overall trend has been positive, with many countries recording growth rates above the global average.
According to data from the International Monetary Fund (IMF), the GDP growth rate for Africa as a whole is expected to increase from 3.2% in 2021 to 4.2% in 2022, signaling a rebound from the economic contraction caused by the COVID-19 pandemic. This growth is expected to be driven by various factors, including increasing commodity prices, improving global demand, and vaccination campaigns against COVID-19.
One country that has recorded significant growth in GDP between 2021 and 2022 is Ghana. The country’s GDP growth rate is expected to increase from 5.7% in 2021 to 7.1% in 2022, driven by robust agricultural production and a rebound in the services sector. This growth is likely to have a positive impact on the country’s GDP per capita, which is projected to rise from $2,223 in 2021 to $2,431 in 2022, according to the World Bank.
Another African country that has recorded significant GDP growth between 2021 and 2022 is Ethiopia. The country’s GDP growth rate is expected to increase from 2.5% in 2021 to 8.7% in 2022, largely due to strong growth in the agriculture and construction sectors. This growth is likely to have a positive impact on the country’s GDP per capita, which is projected to rise from $830 in 2021 to $956 in 2022, according to the World Bank.
On the other hand, some African countries have experienced negative or sluggish GDP growth between 2021 and 2022. For instance, Mozambique’s GDP growth rate is expected to decrease from 1.4% in 2021 to 0.5% in 2022, largely due to the impact of cyclones and the COVID-19 pandemic. This slow growth is likely to have a negative impact on the country’s GDP per capita, which is projected to decline from $523 in 2021 to $505 in 2022, according to the World Bank.
Similarly, Zambia’s GDP growth rate is expected to decrease from 4.4% in 2021 to 2.6% in 2022, largely due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and slow progress in implementing economic reforms. This slow growth is likely to have a negative impact on the country’s GDP per capita, which is projected to decline from $1,222 in 2021 to $1,174 in 2022, according to the World Bank.
It is worth noting that while GDP growth is an important indicator of a country’s economic performance, it does not necessarily reflect the well-being of its citizens. GDP per capita, which is the total GDP of a country divided by its population, is a better indicator of how well citizens are faring economically. A high GDP growth rate does not always translate to a high GDP per capita if the population is growing rapidly, and vice versa.
For example, while Ethiopia is expected to record robust GDP growth between 2021 and 2022, its GDP per capita is still relatively low compared to other African countries. On the other hand, Equatorial Guinea, which is expected to record moderate GDP growth between 2021 and 2022, has a relatively high GDP per capita due to its small population and abundant natural resources.
Future forecast of GDP growth in African countries
The future forecast of GDP growth in African countries is highly dependent on various factors such as economic policies, political stability, natural resources, infrastructure development, and global economic trends. While some African countries have experienced robust GDP growth in recent years, others continue to face economic challenges. Nonetheless, there are reasons to be optimistic about the future of African economies, with several factors pointing towards sustained economic growth in the coming years.
One of the key drivers of future GDP growth in African countries is population growth. According to the United Nations, Africa’s population is projected to double by 2050, reaching 2.5 billion people. While this may pose challenges in terms of providing adequate infrastructure, services, and employment opportunities, it also presents an opportunity for increased consumer demand and a larger workforce. A growing population can translate into increased productivity and economic growth, provided that the right policies and investments are in place to support it.
Another factor that is likely to contribute to future GDP growth in African countries is increased foreign investment. African countries are increasingly seen as attractive investment destinations, thanks to their vast natural resources, improving infrastructure, and a growing consumer market. In recent years, many African countries have implemented economic reforms aimed at improving their business environments and attracting foreign investors. This trend is likely to continue, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, infrastructure development, and renewable energy.
Moreover, the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA), which came into effect in January 2021, is expected to play a significant role in promoting intra-African trade and boosting economic growth. The AfCFTA aims to create a single market for goods and services across the continent, thereby reducing trade barriers and promoting investment. By promoting trade among African countries, the AfCFTA is expected to stimulate economic growth, increase employment, and enhance competitiveness.
Additionally, the digital revolution is set to transform African economies, with increasing access to mobile phones and the internet driving innovation, entrepreneurship, and economic growth. The growth of the digital economy is likely to create new opportunities for African businesses and individuals, from e-commerce and fintech to digital agriculture and healthcare. The increasing availability of digital tools and platforms is also likely to improve efficiency and productivity in various sectors, boosting economic growth.
However, there are also challenges that African countries will need to overcome in order to achieve sustained GDP growth. These challenges include inadequate infrastructure, low levels of education and skill development, corruption, and political instability. Addressing these challenges will require significant investment in infrastructure, education, and governance, as well as greater regional cooperation and coordination.
The future forecast of GDP growth in African countries is positive, with several factors pointing towards sustained economic growth in the coming years. However, African countries will need to address challenges such as inadequate infrastructure, low levels of education and skill development, corruption, and political instability, in order to fully realize their economic potential. With the right policies, investments, and regional cooperation, African countries can achieve inclusive and sustainable economic growth that benefits all citizens.

Team ProdAfrica
team@prodafrica.com