The cocoa industry has played a significant role in the economic development of African countries. In this article, we will discuss the importance of the cocoa industry in Africa, its history, and the challenges faced by the industry.
Cocoa, also known as cacao, is a crop that is native to the tropical regions of South and Central America. The first cocoa plantations in Africa were established in the late 1800s, primarily in the Gold Coast (now Ghana) and Nigeria. Today, Africa is the world’s largest producer of cocoa, accounting for over 70% of the global production.
The cocoa industry is an important source of income for many African countries. It provides employment opportunities for millions of people, from smallholder farmers to large plantation owners. In addition, the cocoa trade generates significant revenue for African economies through exports.
One of the main benefits of the cocoa industry in Africa is its potential to lift people out of poverty. Smallholder farmers who cultivate cocoa beans can earn a decent income, which they can use to support their families and invest in their farms. This income can also help to improve the overall standard of living in rural areas, where most cocoa farms are located.
However, the cocoa industry in Africa faces several challenges. One of the biggest challenges is low productivity. Many cocoa farmers in Africa still use traditional farming methods, which can result in low yields and poor quality beans. This, in turn, affects the profitability of the industry and the livelihoods of those who depend on it.
Another challenge is the prevalence of child labor in the cocoa industry. Children are often used as cheap labor on cocoa farms, especially in West Africa. This practice has been the subject of significant scrutiny and criticism, with many organizations advocating for better working conditions and the eradication of child labor in the cocoa industry.
To address these challenges, various initiatives and programs have been established to support the cocoa industry in Africa. These initiatives include training programs for farmers, the provision of better agricultural inputs, and the promotion of sustainable farming practices. In addition, many chocolate companies have committed to sourcing cocoa beans from sustainable and ethical sources, which can help to improve the working conditions and livelihoods of farmers.
The cocoa industry is a critical component of the African economy, providing employment opportunities and generating significant revenue. However, the industry faces several challenges, including low productivity and the prevalence of child labor. Addressing these challenges requires a concerted effort from all stakeholders, including governments, farmers, and the private sector. By working together, we can help to ensure that the cocoa industry in Africa continues to thrive and benefit the people who depend on it.
The cocoa industry in Africa has not only been a major source of economic growth but has also been responsible for creating numerous employment opportunities. In countries such as Ghana and Cote d’Ivoire, the cocoa industry provides jobs for over two million people. These jobs range from farming to processing, and transportation to exportation. Additionally, it is worth noting that the cocoa industry is often the primary source of income for many rural communities in Africa.
Despite its significance, the cocoa industry in Africa faces numerous challenges that threaten its sustainability. These challenges include low productivity levels, poor infrastructure, disease outbreaks, and environmental degradation. For instance, many cocoa farmers in Africa still use outdated farming techniques that limit their productivity levels. Similarly, the inadequate infrastructure in many cocoa-producing countries makes it difficult to transport cocoa beans from farms to processing plants and eventually to the ports for exportation. These challenges, therefore, need to be addressed to ensure that the cocoa industry in Africa continues to grow and thrive.
The international community also plays a crucial role in the cocoa industry in Africa. The majority of cocoa produced in Africa is exported to the European Union and the United States. Thus, the policies and practices of these regions can significantly impact the cocoa industry in Africa. The international community has a responsibility to promote sustainable practices that protect the environment and support the livelihoods of cocoa farmers and their communities. For instance, initiatives such as Fairtrade and Rainforest Alliance certification aim to promote sustainable cocoa production by providing fair prices to farmers, protecting the environment, and improving working conditions.
This industry in Africa has been a significant contributor to the continent’s economy and provides numerous employment opportunities. However, the industry faces various challenges that need to be addressed to ensure its sustainability. The international community also plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable practices in the cocoa industry in Africa.

- According to the International Cocoa Organization, Africa produced 3.3 million tonnes of cocoa beans in 2020, accounting for over 70% of the world’s total cocoa production.
- Ghana and Cote d’Ivoire are the largest cocoa-producing countries in Africa, with Ghana producing over 900,000 tonnes of cocoa beans and Cote d’Ivoire producing over 2 million tonnes in 2020.
- The cocoa industry is a significant source of revenue for many African countries, with cocoa exports accounting for over 10% of Ghana’s GDP and over 40% of Cote d’Ivoire’s GDP.
- The cocoa industry also provides employment for millions of people in Africa. In Ghana, for instance, the cocoa sector provides jobs for over 800,000 people, while in Cote d’Ivoire, the sector provides jobs for over 2 million people.
- Despite its economic importance, the cocoa industry in Africa faces numerous challenges. For instance, the cocoa swollen shoot virus has been responsible for significant yield losses in many cocoa-producing countries in West Africa. The disease is estimated to cause annual losses of over $700 million in Cote d’Ivoire alone.
- The cocoa industry in Africa also faces environmental challenges. For instance, cocoa farming often leads to deforestation and soil degradation, which can have adverse effects on the environment and the livelihoods of farmers and their communities.
- The international cocoa trade is worth over $100 billion annually, with Europe and the United States being the largest importers of cocoa beans from Africa
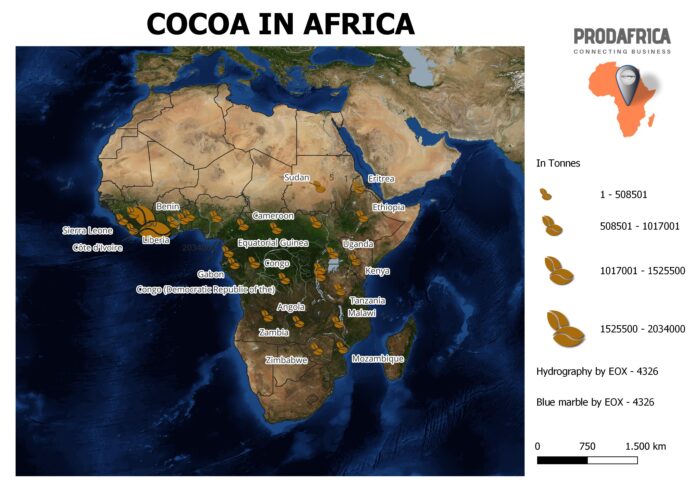
| Country | Cocoa production (tonnes) |
|---|---|
| Côte d’Ivoire | 2,034,000 |
| Ghana | 969,000 |
| Cameroon | 259,000 |
| Nigeria | 250,000 |
| Togo | 109,000 |
| Equatorial Guinea | 50,000 |
| Sierra Leone | 45,000 |
| Gabon | 43,000 |
| Congo | 39,000 |
| Uganda | 35,000 |
| Sao Tome and Principe | 5,500 |
| Liberia | 5,000 |
| Madagascar | 2,500 |
| Zambia | 1,000 |
| Tanzania | 800 |
| Kenya | 600 |
| Guinea | 550 |
| Angola | 500 |
| Central African Republic | 350 |
| Malawi | 300 |
| Zimbabwe | 150 |
| Burundi | 100 |
| Rwanda | 100 |
| Ethiopia | 50 |
| Benin | 30 |
| Mozambique | 20 |
| South Sudan | 15 |
| Congo (Democratic Republic of the) | 10 |
| Sudan | 5 |
| Eritrea | 1 |

Team ProdAfrica
team@prodafrica.com