The internet has become a ubiquitous tool in modern society, with millions of people around the world accessing the web daily to communicate, gather information, and conduct business. While internet access is widespread in developed nations, it has been slower to penetrate many African countries due to a lack of infrastructure and economic resources. However, in recent years, there has been a significant increase in internet penetration in African countries, which has had a profound impact on social, economic, and political development.
The growth of the internet in Africa has been spurred by a combination of factors, including the increasing availability of affordable smartphones, greater investment in telecommunication infrastructure, and the proliferation of social media platforms. According to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the number of internet users in Africa increased from 2.1% in 2005 to 39.3% in 2021, with more than 527 million people now connected to the internet. Despite this impressive growth, however, there are still significant disparities in internet access across the continent, with some countries and regions lagging behind.
One of the main challenges to internet penetration in Africa has been the lack of infrastructure. Many African countries have poor road networks, inadequate power supply, and a limited number of internet service providers (ISPs). These factors have made it difficult to establish the necessary infrastructure to support internet access. However, over the past decade, there has been significant investment in the telecommunication sector in Africa, with mobile network operators (MNOs) and ISPs investing heavily in the expansion of their networks. This investment has enabled the deployment of fiber optic cables, 4G and 5G networks, and the introduction of low-cost smartphones, which have made internet access more affordable and accessible to people in remote areas.
The proliferation of social media platforms has also contributed to the growth of the internet in Africa. Social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have become popular means of communication and have played a significant role in shaping public discourse and political activism in many African countries. For example, during the Arab Spring uprisings, social media played a key role in mobilizing protesters and coordinating their activities. Similarly, in Nigeria, the #EndSARS movement, which aimed to end police brutality, was organized and driven by social media.
The impact of the internet on economic development in Africa has also been significant. The growth of e-commerce platforms has created new opportunities for businesses to reach customers across the continent and has facilitated cross-border trade. For example, Jumia, an online marketplace, operates in 14 African countries and has created thousands of jobs across the continent. Similarly, financial technology (fintech) companies such as M-Pesa in Kenya have enabled millions of people to access financial services, such as banking and insurance, through their mobile phones.
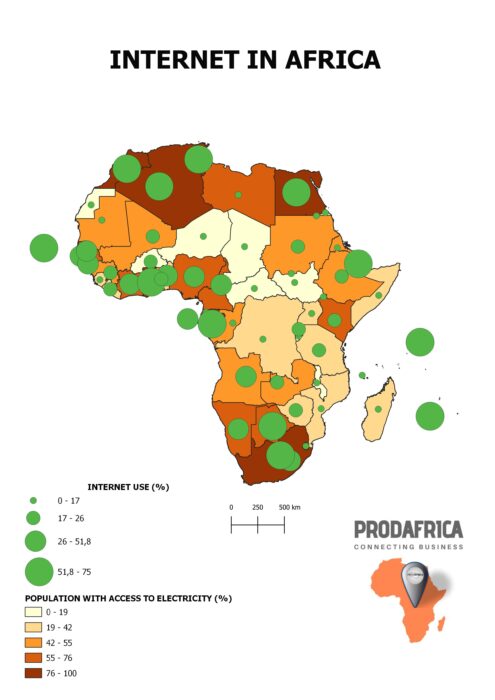
As of 2021, some of the countries with the best internet access in Africa were: Seychelles, Mauritius, South Africa, Morocco, Tunisia, Egypt, Kenya, Nigeria, Rwanda, Ghana, Senegal, Algeria.
It’s worth noting that internet penetration rates can vary widely within countries, with urban areas typically having better access than rural areas. Additionally, internet penetration rates can change rapidly as countries invest in their telecommunications infrastructure and more people gain access to smartphones and other mobile devices.
The internet has also had a transformative impact on education in Africa. With the growth of e-learning platforms, students can now access high-quality educational resources from anywhere in the world. For example, the African Virtual University offers online courses in a range of subjects, from business and economics to science and technology. E-learning platforms have also enabled universities and schools to reach a wider audience and have the potential to improve educational outcomes across the continent.
Despite the significant progress made in internet penetration in African countries, there are still challenges that need to be addressed. One of the main challenges is the high cost of data, which limits access for many people. In addition, the lack of digital literacy and the availability of local content remain significant barriers to internet adoption. Addressing these challenges will require a concerted effort from governments, the private sector, and civil society organizations.
The growth of the internet in African countries has had a profound impact on social, economic, and political development.