
Madrid, the capital city of Spain, has been at the forefront of economic growth in Europe in the past few decades. With its strategic location, favorable business climate, and skilled workforce, Madrid has attracted numerous foreign investments in various sectors, including finance, technology, and infrastructure. However, there is still much potential for further growth and expansion, particularly in emerging markets like the Southern African Development Community (SADC) countries.
The SADC region comprises 16 countries. These countries are rich in natural resources and offer a wealth of opportunities for foreign investors.
It’s worth noting that the Region of Madrid is one of largest economy in the European Union. The region and city has a highly diversified economy with significant contributions from the service, manufacturing, and construction sectors. It is also a major financial center and a hub for international business.
Madrid’s economy in the world based on its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and other economic indicators:
| Economic Indicator | Position in the World |
|---|---|
| PIB nominal (2021) | 39 |
| GDP per capita (2021) | 28th |
| GDP growth rate (2021) | 3.6% |
| Unemployment rate (2021) | 9.1% |
| Inflation rate (2021) | 1.7% |
Madrid
Madrid is a thriving economy and one of the most important economic centers in Europe. The services sector is the backbone of the Madrid economy, accounting for over 80% of the city’s GDP. The city is home to numerous multinational companies and is a leading financial center in Europe. The city’s service sector includes professional services, such as finance, insurance, and real estate, as well as tourism, retail, and healthcare.
The population of the Region of Madrid is approximately 6.75 million in 2021.
Madrid’s GDP grew by 5.0% in 2021. In the same year, the Community of Madrid had a GDP of approximately 34,820 euros per capita, which is the highest among all regions in Spain.
The industrial sector is also an important contributor to Madrid’s economy, accounting for around 10% of the city’s GDP. The city has a diversified industrial base, with significant activities in the automotive, chemical, and electronics industries. Madrid is also home to a number of research and development centers that support innovation and growth in the industrial sector. The region has a highly skilled workforce and a well-developed transport infrastructure that facilitates trade and investment.
IFEMA, the Feria de Madrid, is the city’s leading trade fair venue and plays a vital role in promoting Madrid’s economy. The center hosts over 80 fairs and events each year, bringing together exhibitors and visitors from around the world. IFEMA contributes significantly to the city’s economy, generating over €3 billion in revenue and supporting over 38,000 jobs. The venue is a key driver of the city’s tourism industry, attracting millions of visitors each year.
Trade is also a crucial component of Madrid’s economy, and the city has a well-developed transport infrastructure that facilitates international trade. The Madrid-Barajas Airport is one of the busiest airports in Europe, with direct flights to over 180 destinations worldwide. The city is also home to several major ports and is well-connected to the rest of Europe by road and rail. Madrid’s strategic location and transport links make it an attractive destination for businesses looking to expand their global reach.
Over the last 25 years, Madrid’s economy has undergone significant growth and transformation. According to data from the World Bank, Madrid’s GDP has more than doubled since 1995, growing from $67 billion to over $174 billion in 2021. This growth can be attributed to a number of factors, including strong economic policies, a favorable business environment, and the city’s strategic location as a gateway to Europe and Latin America.
The region has a range of logistics areas that play a crucial role in the transportation and distribution of goods throughout Spain and Europe. Some of the most important logistics areas in Madrid.
- Adolfo Suarez Madrid-Barajas Airport Logistics Park
The Adolfo Suarez Madrid-Barajas Airport Logistics Park is a state-of-the-art facility that serves as a hub for air cargo transportation. The logistics park covers over 250,000 square meters and provides a range of services, including cargo handling, storage, and distribution. The park is strategically located near the airport, making it easy for businesses to transport goods quickly and efficiently.
- San Fernando Logistics Platform
The San Fernando Logistics Platform is a massive logistics center that covers over 1.2 million square meters. The platform provides a range of logistics services, including warehousing, distribution, and transportation. The platform is located near the M-50 and A-4 highways, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Spain and Europe.
- Coslada Logistics Platform
The Coslada Logistics Platform is a modern logistics center that covers over 1.5 million square meters. The platform provides a range of services, including warehousing, distribution, and transportation. The platform is located near the A-2 highway, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Spain and Europe.
- Henares Logistics Platform
The Henares Logistics Platform is a large logistics center that covers over 500,000 square meters. The platform provides a range of logistics services, including warehousing, distribution, and transportation. The platform is located near the A-2 and R-2 highways, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Spain and Europe.
- Getafe Logistics Platform
The Getafe Logistics Platform is a modern logistics center that covers over 400,000 square meters. The platform provides a range of logistics services, including warehousing, distribution, and transportation. The platform is located near the M-50 and A-4 highways, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Spain and Europe.
Southern African Development Community (SADC)
The Southern African Development Community (SADC) is a regional intergovernmental organization that was established in 1980 with the aim of promoting economic development, peace, and security in the southern African region. SADC comprises 16 member states, including Angola, Botswana, Comoros, Democratic Republic of Congo, Eswatini, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritius, Mozambique, Namibia, Seychelles, South Africa, Tanzania, Zambia, and Zimbabwe.
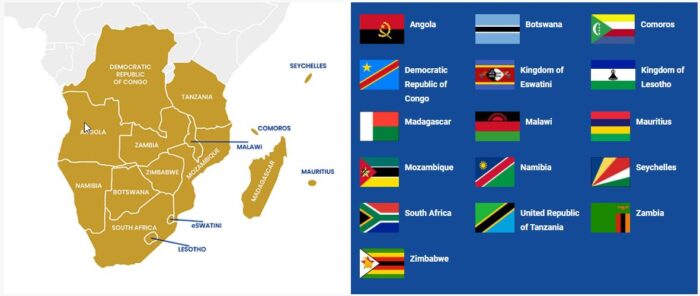
In 2019, the SADC region had a population of 366 million people, according to SADC statistics, and combined a GDP, in 2020, of around US$ 780000 millions.
The organization has a number of objectives, including the promotion of regional integration and cooperation, the reduction of poverty and unemployment, the improvement of infrastructure and transportation, and the development of human resources. SADC also works to promote peace and stability in the region through conflict resolution and prevention initiatives. The organization has made significant progress in achieving these objectives, including the implementation of a free trade area and the establishment of a common market in the region. However, there are still challenges to be addressed, including the need to reduce inequality and poverty, and to address the impact of climate change on the region.
Each country with their own Special Economic Zones Authorities (SEZAs) or similar organizations tasked with promoting and managing SEZs. Here is a list of SEZAs or similar organizations in some of the SADC countries:
- Botswana: Special Economic Zones Authority (SEZA)
- South Africa: Special Economic Zones (SEZ) Program, managed by the Department of Trade, Industry and Competition (DTIC)
- Zambia: Zambia Development Agency (ZDA) oversees SEZs
- Zimbabwe: Special Economic Zones Authority (SEZA)
- Mozambique: Special Economic Zones Office (Gazeda)
- Tanzania: Export Processing Zones Authority (EPZA)
- Malawi: Malawi Investment and Trade Centre (MITC)
- Namibia: Namibia Investment Promotion and Development Board (NIPDB)
- Angola: Investment Promotion Agency (AIPEX)
- Mauritius: Board of Investment (BOI)
- Seychelles: Seychelles Investment Board (SIB)
- Lesotho: Lesotho National Development Corporation (LNDC)
- Eswatini (formerly Swaziland): Eswatini Investment Promotion Authority (EIPA)
These SEZAs or similar organizations are responsible for promoting and managing SEZs in their respective countries, attracting foreign investment, and facilitating economic growth and development. SEZs are seen as important tools for promoting industrialization, export-oriented growth, job creation, and technology transfer in the SADC region.
The region is home to several logistics areas that play a vital role in the transportation and distribution of goods throughout the region and beyond. In this article, we will explore some of the most important logistics areas in SADC.
- Walvis Bay Port, Namibia
The Walvis Bay Port is a deep-water port located on the west coast of Namibia. The port provides a range of services, including container handling, bulk cargo handling, and vehicle handling. The port is strategically located near the Trans-Kalahari and Trans-Caprivi highways, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Southern Africa.
- Beitbridge Border Post, Zimbabwe
The Beitbridge Border Post is the busiest border post in Southern Africa, connecting Zimbabwe and South Africa. The border post provides a range of services, including customs clearance, immigration, and cargo inspection. The border post is strategically located near the N1 highway, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Southern Africa.
- OR Tambo International Airport Cargo Terminal, South Africa
The OR Tambo International Airport Cargo Terminal is a modern facility located in Johannesburg, South Africa. The cargo terminal provides a range of services, including air cargo handling, storage, and distribution. The cargo terminal is strategically located near the N1 and N3 highways, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Southern Africa.
- Kazungula Border Post, Zambia and Botswana
The Kazungula Border Post is a border post connecting Zambia and Botswana. The border post provides a range of services, including customs clearance, immigration, and cargo inspection. The border post is strategically located near the A33 and A3 highways, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Southern Africa.
- Port of Durban, South Africa
The Port of Durban is the busiest port in Southern Africa, located on the east coast of South Africa. The port provides a range of services, including container handling, bulk cargo handling, and vehicle handling. The port is strategically located near the N2 and N3 highways, making it easy for businesses to transport goods to different parts of Southern Africa.
SADC is home to several logistics areas that play a vital role in the transportation and distribution of goods throughout the region and beyond. These logistics areas provide businesses with the infrastructure and services they need to transport goods quickly and efficiently, making SADC a crucial logistics hub in Southern Africa.
Madrid the bridge for the SADC companies to Europe and Latin America markets
Madrid, the vibrant and cosmopolitan capital of Spain, has always been a hub of economic activity and a gateway to Europe and Latin America markets. As a city that embraces innovation and entrepreneurship, Madrid is an ideal partner for companies looking to expand their business in Europe and beyond.
At the same time, the SADC region has also experienced significant economic growth over the past 25 years. According to the African Development Bank, the region’s GDP has grown from $359 billion in 1995 to over $780 billion in 2020. This growth has been driven by a combination of factors, including improved governance, increased investment, and the development of key industries such as mining, agriculture, and tourism.
Given the significant economic growth and potential in both Madrid and the SADC region, there is ample opportunity for increased economic cooperation and investment. By leveraging each other’s strengths and resources, Madrid and SADC countries can create mutually beneficial partnerships that drive growth, create jobs, and contribute to sustainable development.
For companies based in the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region, Madrid offers a unique advantage as a strategic location for reaching out to other European and Latin American markets. Madrid’s well-developed transportation infrastructure and its status as one of the busiest airports in Europe make it an ideal platform for SADC companies to access other markets.
Madrid is also a melting pot of cultures and languages, making it easier for SADC companies to connect with European and Latin American customers. The city’s vibrant business community offers a wealth of opportunities for networking and collaboration, and Madrid’s entrepreneurial spirit and innovative mindset can help SADC companies tap into new markets and technologies.
Madrid’s growing economy and its strategic location make it an ideal partner for SADC countries looking to expand their reach in Europe and Latin America. With a population of over 6 million a, Madrid is one of the largest and most dynamic economies in Europe. The city is home to a diverse range of industries, including technology, finance, and tourism, which can provide valuable opportunities for SADC companies seeking to enter new markets.
Spain has been one of the top trading partners of SADC countries in recent years, with bilateral trade increasing significantly. The trade volume between Spain and SADC countries was valued at over €12 billion in 2020, representing a substantial increase from previous years. Madrid, being the economic powerhouse of Spain, has played a significant role in strengthening economic ties with SADC countries.
In terms of investment, Madrid-based companies have been investing in various sectors in SADC countries, such as renewable energy, mining, and infrastructure. Spanish companies such as Acciona, Endesa, and Grupo Cobra have established a presence in the region, and more Madrid-based firms are expected to follow suit.
Points about the economic relations between Madrid and Sudafrican countries
- South Africa is the largest economy in the region, and Madrid maintains strong economic ties with the country. The two have been trading partners for many years, with Madrid importing a variety of goods from South Africa, including precious metals, fruits, and wines.
- The Spanish government has established a number of trade agreements with South Africa and other countries in the region to encourage trade and investment. These agreements help to remove barriers to trade and provide incentives for businesses in both countries to expand their operations.
- Madrid is home to a number of Spanish companies that operate in South Africa and other countries in the region. These companies are involved in a variety of sectors, including telecommunications, energy, infrastructure, and consumer goods.
- Madrid has a well-developed financial services sector, and many South African companies have established partnerships with Spanish banks and other financial institutions. This helps to facilitate trade and investment between the two countries.
- In recent years, there has been an increase in tourism between Madrid and South Africa. Madrid is a popular destination for South African tourists, who come to explore the city’s historic sites, museums, and cultural attractions. Similarly, many Spanish tourists are attracted to South Africa’s natural beauty, wildlife, and adventure activities.
- There are also cultural and educational ties between Madrid and South African countries. Many South Africans study in Madrid, and there are numerous cultural exchange programs that promote understanding and collaboration between the two regions.
- Despite these strong economic ties, there are also challenges to be addressed. These include issues related to political instability, corruption, and inequality in some South African countries, as well as concerns about protectionism and trade barriers in some sectors.
Overall, the economic relations between Madrid and South African countries are diverse and multifaceted, with opportunities for trade, investment, and cultural exchange. While there are challenges to be addressed, there is also great potential for continued growth and collaboration between the two regions
GDP rankings and GDP per capita of SADC countries in the world:
| Country | GDP (nominal) in USD (2021) | World GDP Rank | GDP per capita (nominal) in USD (2021) | World GDP per capita Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Africa | 372.9 billion | 36 | 6,276 | 104 |
| Angola | 105.3 billion | 67 | 3,109 | 145 |
| Tanzania | 63.2 billion | 85 | 1,056 | 183 |
| Zambia | 38.4 billion | 111 | 2,062 | 156 |
| Zimbabwe | 24.5 billion | 131 | 1,520 | 169 |
| Mozambique | 15.3 billion | 157 | 505 | 224 |
| Botswana | 8.5 billion | 166 | 3,498 | 138 |
| Namibia | 7.4 billion | 174 | 3,019 | 152 |
| Eswatini | 4.5 billion | 194 | 3,834 | 129 |
| Lesotho | 2.8 billion | 208 | 1,326 | 176 |
| Madagascar | 2.6 billion | 213 | 109 | 235 |
| Malawi | 2.1 billion | 226 | 104 | 237 |
It’s important to note that GDP rankings and GDP per capita can vary depending on the source and the specific year being considered.
However, there is still much potential for further investment in SADC countries, particularly in sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and tourism. These sectors offer tremendous opportunities for Madrid-based companies to invest in and expand their businesses.
Moreover, Madrid is home to many leading companies in the technology and innovation sectors, which could be leveraged to support SADC countries’ economic development. The Madrid-based tech companies have the expertise to develop and implement cutting-edge technologies in sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and renewable energy, which could help increase productivity and promote economic growth in SADC countries.
Madrid International Airport – SADC
Madrid International Airport, also known as Adolfo Suárez Madrid-Barajas Airport, is one of the most important air transport hubs in Europe. Located in the northeast of Madrid, the airport has four terminals and handles a large number of domestic and international flights. As a result of its strategic location, Madrid Airport serves as a major gateway between Europe and Latin America, as well as Africa and the Middle East.
The airport is operated by Aena, which is the world’s largest airport operator by passenger numbers, and has been continuously expanding its services and infrastructure over the years. The airport’s capacity has grown significantly, and it now handles over 61 million passengers annually. Madrid Airport is well-connected to the city center via a range of transportation options, including metro, train, bus and taxi services. As such, it has become a key driver of economic growth in the region, creating jobs and attracting investment from around the world.
In terms of air connectivity, Madrid International Airport provides excellent connections to major SADC cities such as Johannesburg, Cape Town, and Luanda. This connectivity provides a gateway for Madrid-based businesses to enter SADC countries and tap into the numerous opportunities that the region offers.
| Country | Airport | Total Passengers (2019) | Passengers to Madrid (2019) | Passengers from Madrid (2019) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| South Africa | OR Tambo International Airport | 21,950,000 | 24,200 | 23,300 |
| Angola | Quatro de Fevereiro International Airport | 1,731,086 | 1,100 | 1,300 |
| Mozambique | Maputo International Airport | 887,698 | 1,400 | 1,200 |
| Botswana | Sir Seretse Khama International Airport | 1,778,650 | 800 | 600 |
| Zimbabwe | Robert Gabriel Mugabe International Airport | 839,912 | 1,300 | 1,200 |
| Namibia | Hosea Kutako International Airport | 744,883 | 800 | 1,100 |
| Zambia | Kenneth Kaunda International Airport | 1,294,446 | 400 | 500 |
Furthermore, Madrid has a sizable expatriate community living in SADC countries. This community comprises mainly business executives, entrepreneurs, and professionals who have relocated to the region for work or investment opportunities. Their presence in the region offers a significant advantage for Madrid-based companies seeking to establish a presence in SADC countries.
Some Spanish companies based in Madrid that operate in SADC
There are several reasons why Madrid-based companies and SADC companies choose to operate in each other’s respective regions. For Madrid companies, SADC countries offer a largely untapped market with enormous growth potential. The region is rich in natural resources and has a young, growing population. Furthermore, several SADC countries have made strides in creating a more business-friendly environment, which has attracted foreign investment. For Madrid companies looking to expand internationally, SADC countries provide a relatively low-risk opportunity for growth in a region with strong potential.
For SADC companies, Madrid offers a gateway to the rest of Europe and the Latin American market. Spain has a strategic location at the crossroads of Europe, Africa, and the Americas, and is a natural bridge between these regions. Madrid, as the capital and largest city in Spain, is an important hub for businesses looking to expand their reach. The city offers a skilled workforce, modern infrastructure, and a business-friendly environment. In addition, Spain has strong economic ties with Latin American countries, which opens up new opportunities for SADC companies looking to expand beyond their home region.
Some examples of Spanish companies based in Madrid that operate in the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region:
- Banco Santander: This Spanish multinational banking and financial services company has a presence in several SADC countries, including South Africa, Mozambique, and Angola.
- Telefonica: This Spanish telecommunications company operates in several SADC countries, including South Africa, Namibia, and Angola.
- Acciona: This Spanish conglomerate with interests in infrastructure, renewable energy, and water management has projects in several SADC countries, including South Africa, Zambia, and Mozambique.
- Ferrovial: This Spanish multinational company operates in the infrastructure and construction sectors and has projects in several SADC countries, including South Africa and Mozambique.
- BBVA: This Spanish multinational banking group has a presence in several SADC countries, including South Africa and Mozambique.
- Mapfre: This Spanish multinational insurance company has operations in several SADC countries, including South Africa, Angola, and Mozambique.
- Iberdrola: This Spanish multinational electric utility company has renewable energy projects in several SADC countries, including South Africa and Mozambique.
Some examples of SADC companies based in Madrid region:
- Sasol: This South African energy company has a presence in Madrid and operates in the areas of oil and gas exploration, production, and marketing.
- Shoprite Holdings: This South African retail giant has a presence in Madrid through its subsidiary, Shoprite Checkers España, which operates several grocery stores in the city.
- Investec: This South African specialist bank and asset manager has a presence in Madrid and offers a range of financial services to clients in Spain and beyond.
- Anglo American: This South African mining company has a presence in Madrid and operates in the areas of platinum, diamonds, and copper.
- Woolworths Holdings: This South African retail company has a presence in Madrid through its subsidiary, David Jones, which operates several luxury department stores in the city.
- Bidvest Group: This South African services, trading, and distribution company has a presence in Madrid and operates in the areas of food, automotive, and financial services.
- Standard Bank: This South African financial services group has a presence in Madrid and offers a range of banking and investment services to clients in Spain and beyond.
Others African companies based in SADC countries that operate in Madrid:
Nampak (South Africa), Eskom (South Africa), MTN Group (South Africa) Nedbank (South Africa), Pick n Pay (South Africa), FNB (South Africa), Barloworld (South Africa), Transnet (South Africa), Tongaat Hulett (South Africa), Vodacom Group (South Africa), Massmart Holdings (South Africa), Liberty Holdings (South Africa), Old Mutual (South Africa), M-Pesa (Kenya), BGI Group (Botswana), African Rainbow Minerals (South Africa), PPC Limited (South Africa), Coronation Fund Managers (South Africa)
Economic relations between Madrid and the countries of the Southern African Development Community (SADC)
| Country | Export from Madrid | Import to Madrid | Key sectors |
|---|---|---|---|
| South Africa | Machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals | Wine, fruits, ores, chemicals, machinery | Infrastructure, renewable energy, telecommunications, financial services |
| Angola | Machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals | Petroleum, diamonds, coffee, fruits | Infrastructure, construction, energy, telecommunications |
| Mozambique | Machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals | Petroleum, natural gas, aluminum, cashews, coal | Infrastructure, renewable energy, water management, construction |
| Botswana | Machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals | Diamonds, copper, nickel, beef | Mining, financial services, tourism, agriculture |
| Zimbabwe | Machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals | Tobacco, diamonds, gold, platinum, textiles | Mining, agriculture, manufacturing, tourism |
| Namibia | Machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals | Fish, diamonds, uranium, beef | Mining, tourism, agriculture, fisheries |
| Zambia | Machinery, vehicles, electronics, pharmaceuticals | Copper, cobalt, tobacco, maize | Mining, agriculture, tourism, manufacturing |
Economic relations between Madrid and the countries of the Southern African Development Community (SADC), including import and export quantities in dollars:
| Country | Export from Madrid (USD) | Import to Madrid (USD) | Key sectors |
|---|---|---|---|
| South Africa | 161.6 million | 326.8 million | Infrastructure, renewable energy, telecommunications, financial services |
| Angola | 18.3 million | 22.5 million | Infrastructure, construction, energy, telecommunications |
| Mozambique | 10.6 million | 16.8 million | Infrastructure, renewable energy, water management, construction |
| Botswana | 9.2 million | 1.2 million | Mining, financial services, tourism, agriculture |
| Zimbabwe | 6.7 million | 9.9 million | Mining, agriculture, manufacturing, tourism |
| Namibia | 3.2 million | 2.3 million | Mining, tourism, agriculture, fisheries |
| Zambia | 1.9 million | 8.6 million | Mining, agriculture, tourism, manufacturing |
Strategic areas where Madrid-based companies may consider investing in SADC countries
Of course, the specific opportunities and challenges in each SADC country will vary, so it is important for companies to conduct thorough market research and engage with local stakeholders to identify the most promising areas for investment.
- Infrastructure development, including roads, bridges, ports, and airports
- Energy, particularly renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power
- Agriculture and food production, including the development of new technologies and techniques for sustainable farming
- Mining and natural resources, particularly in countries with large reserves of minerals and metals such as South Africa and Angola
- Tourism, particularly in countries with unique cultural and natural attractions such as Tanzania and Mozambique
- Telecommunications and information technology, including the development of new networks and technologies to connect people and businesses across the region
- Healthcare, including the development of new treatments and technologies to address the health challenges facing many SADC countries
- Education and training, particularly in areas such as vocational training and skills development to help build a skilled workforce and support economic growth.
Economic exchange between Spain and SADC countries, based on 2019 data from the Spanish Ministry of Foreign Affairs, European Union, and Cooperation:
| Country | Imports from SADC (million euros) | Exports to SADC (million euros) |
|---|---|---|
| South Africa | 1,836 | 1,471 |
| Angola | 307 | 637 |
| Namibia | 107 | 72 |
| Mozambique | 54 | 88 |
| Zambia | 33 | 43 |
| Zimbabwe | 13 | 26 |
| Botswana | 11 | 28 |
| Tanzania | 8 | 31 |
| Malawi | 5 | 2 |
| Madagascar | 5 | 5 |
| Mauritius | 4 | 43 |
| Swaziland | 2 | 1 |
| Lesotho | 1 | 2 |
Some final conclusions
Madrid’s economic potential and expertise, coupled with the opportunities offered by the SADC region, create a promising outlook for increased economic cooperation and investment. With the right policies and strategies, Madrid-based companies can leverage their expertise to support economic development in SADC countries while also benefiting from the region’s growth potential. Madrid has much to offer the SADC region, and the region offers an exciting opportunity for Madrid to expand its businesses and strengthen its economic ties.
Madrid serves as a crucial bridge for SADC countries to connect with the rest of Europe and Latin America markets. The city has a strong economy and is home to many prominent companies in various sectors, making it an attractive investment destination for SADC companies looking to expand their business abroad. By tapping into Madrid’s expertise and resources, SADC countries can gain a competitive advantage in the global market.
The economic potential of the SADC countries is immense, with a combined GDP of over $700 billion. However, the region’s economic growth has been uneven, with some countries performing better than others. By partnering with Madrid, SADC countries can access new opportunities to accelerate their economic growth and development. The city’s expertise in sectors such as finance, technology, and renewable energy can help SADC countries to diversify their economies, create new industries and generate more employment opportunities.
Madrid’s commitment to promoting economic cooperation and investment in SADC countries has been significant. The city has established several initiatives aimed at strengthening economic ties between Madrid and SADC countries. The Madrid Business Forum, for instance, provides a platform for business leaders from both regions to exchange ideas and explore new investment opportunities. The Madrid International Trade Fair (IFEMA), on the other hand, brings together companies from all over the world to showcase their products and services, creating new business opportunities for SADC countries.
In conclusion, Madrid has a lot to offer SADC countries, and by collaborating, both regions can benefit significantly. With its strategic location, world-class infrastructure, and robust economy, Madrid is the ideal partner for SADC companies looking to expand their business abroad. The city’s commitment to promoting economic cooperation and investment in SADC countries demonstrates its dedication to building a mutually beneficial relationship that can contribute to the development and growth of both regions.
Contact details
ProdAfrica Business Directory: team@prodafrica.com
Investment departments of the Madrid Council and the Community of Madrid:
| Department Name | City | Phone | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Madrid Investment Attraction Office | Madrid | +34 91 588 65 57 | invest@madrid.es |
| Madrid Emprende | Madrid | +34 91 364 65 77 | info@madridemprende.es |
| Invest in Madrid | Madrid | +34 91 538 38 38 | info@investinmadrid.com |
| Madrid Investment Promotion Agency (APIE) | Madrid | +34 91 720 69 60 | info@apie.es |
Investment departments or investment ministries of the SADC African countries along with their name, city, phone number, and email:
| Country | Department/Ministry Name | City | Phone | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Southern African Development Community (SADC) | Gaborone | +267 395 1863 | prinfo@sadc.int | |
| Angola | Ministry of Economy and Planning | Luanda | +244 222 390 399 | mep@minec.gov.ao |
| Botswana | Botswana Investment and Trade Centre | Gaborone | +267 36 3200 | invest@bitc.co.bw |
| Comoros | Ministry of Finance, Budget and Investment | Moroni | +269 773 88 28 | sfbi@comorestelecom.km |
| Eswatini | Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Trade | Mbabane | +268 2404 5172 | info@mcit.gov.sz |
| Democratic Republic of Congo | Agency for the Promotion of Investment in Congo (API) | Kinshasa | +243 99 702 0040 | info@api.gouv.cd |
| Lesotho | Ministry of Trade and Industry | Maseru | +266 2232 3714 | info@moti.gov.ls |
| Madagascar | Agency for Business Development and Investment Promotion | Antananarivo | +261 34 05 299 36 | adbpmadagascar@gmail.com |
| Malawi | Malawi Investment and Trade Centre | Lilongwe | +265 1 771 315 | info@mitc.mw |
| Mauritius | Economic Development Board Mauritius | Port Louis | +230 203 3800 | contactus@edbmauritius.org |
| Mozambique | Investment and Export Promotion Agency of Mozambique | Maputo | +258 21 480 446 | info@apex.co.mz |
| Namibia | Ministry of Industrialisation and Trade | Windhoek | +264 61 283 7338 | invest@mit.gov.na |
| Seychelles | Department of Investment, Entrepreneurship Development and Business Innovation | Victoria | +248 428 2000 | info.invest@finance.gov.sc |
| South Africa | Department of Trade, Industry and Competition | Pretoria | +27 12 394 9500 | contactus@dtic.gov.za |
| Tanzania | Tanzania Investment Centre | Dar es Salaam | +255 22 211 6328 | tic@tic.co.tz |
| Zambia | Zambia Development Agency | Lusaka | +260 211 229 725 | info@zda.org.zm |
| Zimbabwe | Zimbabwe Investment and Development Agency | Harare | +263 4 794 771 | info@zida.co.zw |

Juan Esteban Reina
EuroManager
ProdAfrica Business Directory & Consulting